Large Language Models: Bridging the Gap in Cybersecurity
Large language models (LLMs) have become an indispensable tool in cybersecurity, offering significant solutions to the challenges facing Security Operations Center (SOC) analysts. By simulating human-level performance, these advanced AI models are truly transforming the field. At IntelliGenesis, our developers and data scientists are already incorporating LLM capabilities into tools like KrakenAI™, our cybersecurity-focused LLM platform that delivers real-time assistance to cybersecurity analysts and incident response teams defending critical networks.
So, what exactly are large language models? In simple terms, LLMs are powerful artificial intelligence tools that use neural networks, massive datasets, and natural language processing to accomplish all sorts of tasks—from generating text and translating languages to summarizing information. At their core, these models learn to make predictions based on the data they’ve been trained on.
The evolution of LLMs is an interesting story. It started in the 1950s and ‘60s with rule-based systems that could simulate conversations but were robotic because they relied on preset patterns. Fast forward to the 1990s, and there was a big shift towards statistical approaches that began to understand language better. Then came the n-gram models in the late ‘90s and early 2000s, which focused on word sequences, relationships between words, and relevance ranking to understand context.
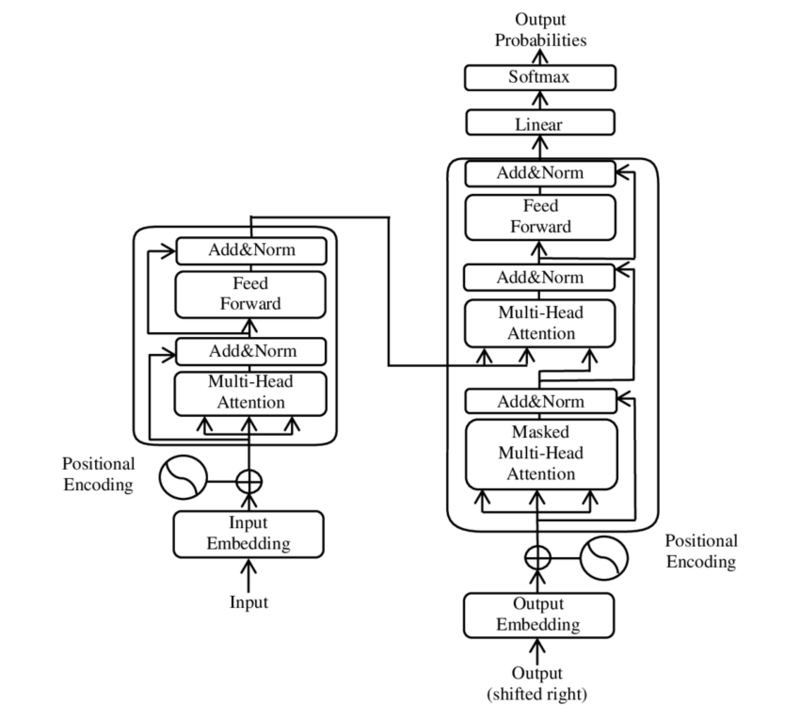
The real game-changer, though, was the “Transformer” architecture introduced in 2017. This allowed LLMs to process sequences in parallel and understand long-range dependencies, leading to significant improvements in language processing. Models like BERT, GPT, and the latest GPT-4 have continued to push the boundaries, showcasing an incredible ability to generate coherent, contextually rich text and multimodal capabilities.1
And the best part? These LLMs are now playing a valuable role in the world of cybersecurity. Here are a few of the practical applications:
- Threat Intelligence Analysis: LLMs can sift through large amounts of threat data to uncover the key insights that help SOC analysts stay ahead of emerging threats. By analyzing this data, LLMs can uncover new attack methods and tactics used by cyber adversaries.
- Anomaly Detection: Using deep learning, LLMs can spot unusual patterns in network traffic and system logs. These models can spot deviations from normal behavior with high accuracy, which is crucial for catching potential cyber threats like security breaches, data exfiltration attempts, or unauthorized access in real-time, before they turn into major incidents.
- Malware Detection: Legacy signature-based antivirus solutions can struggle to keep up with the fast-paced emergence of new malware variants. LLMs can be trained to recognize malware signatures and behaviors using deep learning techniques, which boosts malware detection accuracy, making it easier to classify and quarantine malicious software.
- Phishing Detection: LLMs enhance phishing detection by analyzing email contents and spotting suspicious patterns, offering effective protection against sophisticated scams that often slip through traditional security measures.
- Incident Response and Automation: The ability of LLMs to understand and generate human-like text makes them great for incident response. They can automate the creation of detailed incident reports, summarize incidents, suggest remediation steps, and identify documentation gaps.
The list goes on—large language models can be applied to code review, red teaming, simulated environments, and more. But what makes LLMs so powerful in the cybersecurity domain? A few key reasons:
- Contextual Understanding: LLMs can function as conversational “co-pilots,” providing real-time, contextual support to security analysts.
- Democratizing Security Skills: LLMs can explain complex technical concepts in plain language, empowering even non-expert analysts to detect, investigate, and respond to cyber threats.
- Continuous Learning: LLMs are designed to keep learning and adapting, ensuring they stay effective in the ever-changing cybersecurity landscape.
- Integration with Existing Tools: LLMs can enhance the capabilities of current cybersecurity tools and platforms, without requiring major changes to the existing setup.
- Efficiency and Scalability: LLMs can be optimized to run efficiently on various hardware setups, from local CPUs to cloud-based GPUs.
Enter KrakenAI from IntelliGenesis’ IG Labs—a cybersecurity solution that harnesses the power of LLMs to tackle the unique challenges faced by SOC analysts. Here’s how KrakenAI boosts cybersecurity operations:
- Conversational AI Tool: KrakenAI acts as a virtual cybersecurity expert, providing analysts with detailed, context-rich answers to their questions. It also serves as an advanced training tool that helps bridge gaps in cybersecurity skills and regulatory compliance.
- Adaptive Learning: KrakenAI’s cognitive-based approach ensures it keeps learning and adapting to new threats, delivering up-to-date intelligence and improving the decision-making process.
- Model Training and Integration: The effectiveness of KrakenAI is rooted in its comprehensive model training, which incorporates a wide range of datasets critical for cybersecurity. It integrates seamlessly with other third-party cybersecurity tools, enhancing the capabilities of existing systems and ensuring analysts have access to the latest threat intelligence.
- Tackling Operational Challenges: KrakenAI addresses the limitations of generic AI platforms by using known-safe data, which ensures operational security and also limits hallucinations.
- Security and Privacy-Preserving Technologies: KrakenAI uses advanced techniques to ensure data privacy, resilience against attacks, and protection against data poisoning attempts.
Large language models are redefining the security landscape by dramatically augmenting human capabilities to accomplish tasks that were traditionally time-consuming and prone to error. But there are still many challenges to overcome. KrakenAI was developed to optimize the current abilities of LLMs while being mindful on their inherent risks and limitations.
- Image of the illustration of the components of the Transformer model from the original paper – Xiong, Ruibin; Yang, Yunchang; He, Di; Zheng, Kai; Zheng, Shuxin; Xing, Chen; Zhang, Huishuai; Lan, Yanyan; Wang, Liwei; Liu, Tie-Yan (2020-06-29). “On Layer Normalization in the Transformer Architecture” ↩︎